We are studying Photonic Integrated Circuits. ▷Japanese
7-1, Kioi-cho, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 102-8554
Room 4-275A
Glossary
- WDM: Wavelength Division Multiplexing
- Refractive index change in semiconductor material
| Physical effect | |
| Temperature change | Thermo-Optic effect |
| Current injection | Burstain-Moss effect |
| Plasma effect | |
| Bandgap shrinkage | |
| Applied electric field | Franz-Keldysh |
| Quantum confined stark effect |
| Speed | Consumption power | Wavelength dependence | |
| TO effect | △ | △ | ◎ |
| Plasma effect | ○ | △ | ◎ |
| Burstain-Moss effect | ○ | △ | △ |
| QCSE | ◎ | ◎ | △ |
- Kramers-Kronigh relationship
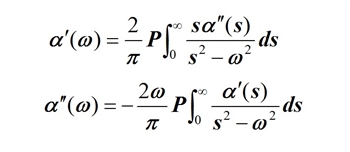
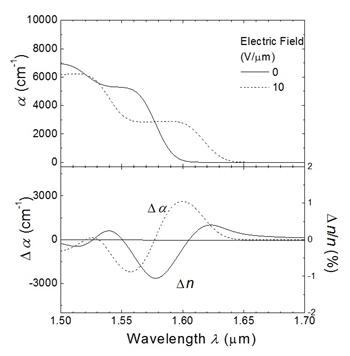
When the electric field is applied to the semiconductor material, the absorption edge wavelength is shifted to the longer wavelength by the Franz-Keldysh or QCSE effect, and the refractive index is changed at the same time. The following figure shows the refractive index change and absorption change as a function of wavelength.
バナースペース
Shimolab
7-1, Kioi-cho, Chiyoda-ku,
Tokyo 102-8554
Room 4-275A